What is diabetes?
Diabetes occurs when your blood sugar is too high due to a lack of insulin production or the body not responding well to insulin. It can affect anyone and can be managed with medication and lifestyle adjustments.
What are the types of diabetes?
- Type 1 diabetes – develops when your body does not make enough insulin or any insulin at all.
- Type 2 diabetes – mainly results from insulin resistance. Insulin resistance happens when your muscles, fat tissue, and liver do not respond well to insulin. Obesity, lack of physical activity, unhealthy diet, hormonal imbalances, genetics, and certain medications would contribute to the development of this. It is the most common type.
- Gestational diabetes – a special type of diabetes that can occur in pregnancy in some women.
Several other types of diabetes have been identified, but those types are relatively rare.
What are the symptoms of diabetes?

Symptoms of diabetes include:
- Increased thirst and dry mouth
- Increased hunger
- Frequent urination / nocturia
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Unexplained weight loss
- Numbness or tingling in your hands or feet
- Slow-healing sores or cuts
- Frequent skin and/or vaginal yeast infections
Some of the individuals do not develop symptoms and they are detected at routine checkups.
Some can present as a medical emergency which is called diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA). Symptoms include vomiting, abdominal pains, fruity-smell breath, and shortness of breath.
How to diagnose diabetes?

When you present with the above symptoms or when you have risk factors your doctor will order a few blood tests. Those blood tests are fasting blood sugar (FBS), HbA1c, and random blood sugar (RBS). A special test called OGTT (Oral Glucose Tolerance Test) is done if you are pregnant.
Cut-off values used for the diagnosis are FBS > 126 mg/dL and HbA1c > 6.5%. A random blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher indicates diabetes.
FBS – You will need to fast at least 8-10 hours before the test. You should not eat or drink anything except for water (a non-caloric drink).
Two abnormal tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis unless you have the classic symptoms of diabetes.

What is pre-diabetes?
Pre-diabetes is diagnosed when your blood tests are above normal but below the cut-off values of diabetes.
FBS is 100 – 125 mg/dL or
HbA1c is 5.7% – 6.4%.
If you have pre-diabetes, you have a higher risk of future development of diabetes. Adhering to a healthy lifestyle would mitigate the risk of developing diabetes.
How to treat diabetes?
Both lifestyle modifications and medications are equally important in the management of diabetes. Lifestyle modifications include;
- Eating a healthy diet
- Regular physical exercise
- Adequate overnight sleep
- Quit smoking and avoid alcohol
- Living a stress-free life
Eating the right amount of carbohydrates at each meal is very important.
Avoid refined sugars and sweets.
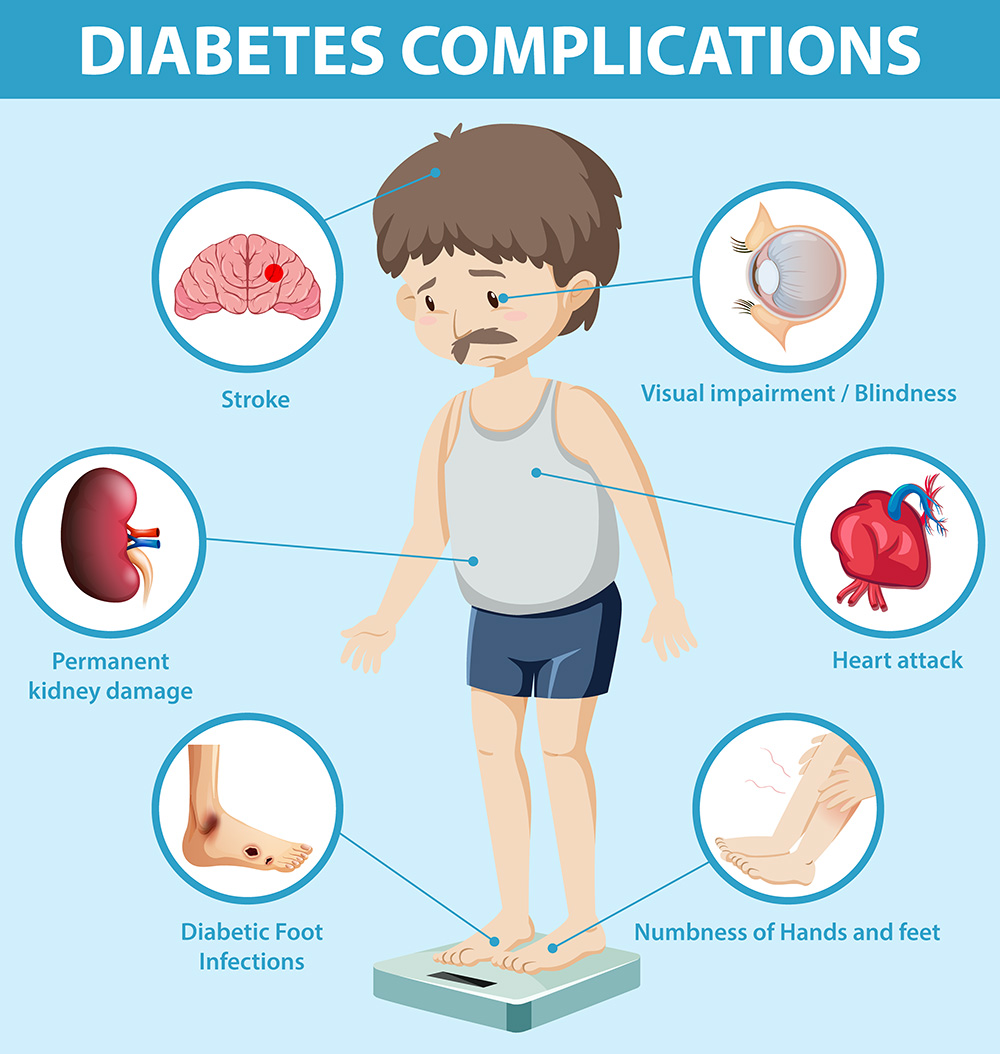
Complications
Diabetes is a disease that can cause dysfunction of many vital organs.




 info@slcim.com
info@slcim.com